Title: Understanding the Power of Din Rail Breakers: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction:
In the dynamic world of electrical systems, efficiency, safety, and adaptability are paramount. One crucial component that plays a pivotal role in ensuring the smooth functioning of electrical circuits is the Din Rail Breaker. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the key aspects of Din Rail Breakers, exploring their purpose, advantages, installation, and the impact they have on electrical systems.
What is a Din Rail Breaker?
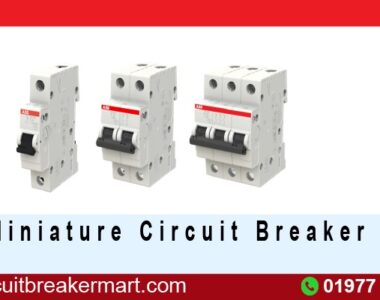
Din Rail Breakers, also known as miniature circuit breakers (MCBs), are essential components in electrical distribution systems. These devices are designed to protect circuits and electrical equipment from overloads and short circuits. The term “Din Rail” refers to the standardized mounting rail on which these breakers are installed, allowing for a modular and space-efficient arrangement in control panels and distribution boards.
Key Features and Advantages:
- Overload Protection: Din Rail Breakers are equipped with thermal-magnetic trip elements that respond to both overcurrents (overloads) and short circuits. This dual protection mechanism ensures a swift response to various fault conditions, preventing damage to connected devices.
- Compact Design: The compact size of Din Rail Breakers allows for high-density installations, making them ideal for applications where space is a premium. The standardized Din Rail mounting also facilitates easy installation and replacement.
- Modularity: The modular nature of Din Rail Breakers simplifies maintenance and upgrades. Individual breakers can be added or replaced without affecting the entire system, providing a cost-effective and scalable solution.
- Ease of Installation: Installing Din Rail Breakers is a straightforward process. They snap onto the Din Rail, eliminating the need for complex mounting procedures. This ease of installation translates to time and cost savings during system setup and maintenance.
Types of Din Rail Breakers:
- Single-Pole Breakers: These breakers interrupt the current flow in a single conductor and are commonly used for low-voltage applications.
- Double-Pole Breakers: Designed to interrupt the current flow in both conductors of a single-phase circuit, double-pole breakers are suitable for applications requiring higher voltage protection.
- Three-Pole Breakers: These breakers are used in three-phase systems, providing protection for each phase. They are crucial for maintaining balance and preventing overloads in multi-phase installations.
Installation Tips:
- Proper Sizing: Select Din Rail Breakers with the appropriate current rating for the circuits they are protecting. Undersized breakers may not provide adequate protection, while oversized breakers may not trip during faults.
- Labeling and Documentation: Ensure that each Din Rail Breaker is properly labeled, indicating the circuit it protects. This aids in troubleshooting, maintenance, and emergency response.
- Regular Inspection: Periodically inspect Din Rail Breakers for signs of wear, damage, or overheating. Replace any defective breakers promptly to maintain the integrity of the electrical system.
Conclusion:
In the realm of electrical distribution systems, Din Rail Breakers stand as stalwart guardians, ensuring the smooth flow of power while safeguarding against potential hazards. Their compact design, modularity, and efficiency make them indispensable components in control panels and distribution boards across various industries. By understanding the key features, advantages, and installation considerations of Din Rail Breakers, electrical professionals can harness their power to create resilient and reliable electrical systems.
Din Rail Breakers:
- “Din Rail Breakers: Essential Guide for Electrical Systems”
- “Miniature Circuit Breakers: Benefits and Installation Tips”
- “Din Rail MCBs: Compact Design and Overload Protection”
- “Electrical System Safety: Din Rail Breaker Advantages”
- “Modular Din Rail Breakers: Space-Efficient Solutions”
- “Din Rail Breaker Types: Single, Double, and Three-Pole”
- “Efficient Electrical Distribution: Din Rail Breaker Insights”
- “MCB Installation Tips: Ensuring Proper Circuit Protection”
- “Compact and Reliable: Din Rail Breakers Explained”
- “Upgrade Your System: Din Rail Breakers for Modern Electrical Solutions”