Title: Unveiling the Power Within A Deep Dive into Molded Case Circuit Breakers
In the intricate web of electrical systems, Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs) stand as stalwart guardians, ensuring the safe and efficient flow of power. This comprehensive guide aims to unravel the intricacies of MCCBs, shedding light on their construction, functionality, applications, and the indispensable role they play in modern electrical infrastructure.
Understanding Molded Case Circuit Breakers:
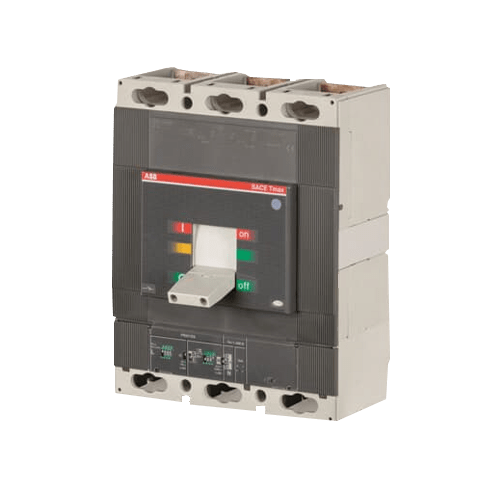
Construction: MCCBs are aptly named for their molded case, typically made from insulating materials like thermosetting plastics. Within this robust casing lies a combination of conductive and insulating components designed to interrupt electrical currents under fault conditions.
Working Principle: At the heart of every MCCB is a trip unit, responsible for sensing overcurrents and responding promptly to protect the connected electrical circuit. The trip unit can be thermal, magnetic, or a combination of both, providing a versatile approach to circuit protection.
Key Features and Advantages:
- Overcurrent Protection: MCCBs excel at safeguarding against overcurrents, whether caused by excessive loads or short circuits. Their quick response helps prevent damage to equipment and ensures the safety of the electrical system.
- Adjustable Settings: One notable feature of MCCBs is their adjustable trip settings. This flexibility allows for fine-tuning based on the specific requirements of the connected circuit, providing a tailored approach to protection.
- Remote Control and Monitoring: In the era of smart technology, many MCCBs come equipped with remote control and monitoring capabilities. This not only enhances convenience but also enables proactive management of electrical systems.
- Compact Design: The molded case not only provides robust protection but also contributes to the compact design of MCCBs. This is especially valuable in applications where space is at a premium.
Applications and Industry Use:
- Commercial Buildings: MCCBs find widespread use in commercial buildings for protecting distribution panels and electrical systems. Their reliability and adaptability make them a cornerstone in ensuring an uninterrupted power supply.
- Industrial Settings: In industrial environments, MCCBs play a crucial role in safeguarding heavy machinery and equipment. Their ability to handle high currents and diverse fault conditions makes them indispensable in manufacturing facilities.
- Renewable Energy Installations: With the growing emphasis on renewable energy, MCCBs are integral to the protection of solar and wind power systems. Their versatility makes them well-suited for the dynamic conditions of alternative energy sources.
Installation and Maintenance:
- Proper Sizing: Correctly sizing MCCBs is paramount. It requires a thorough understanding of the connected load, potential fault currents, and the specific characteristics of the electrical system.
- Regular Inspections: Periodic inspections of MCCBs are essential to ensure proper functioning. Visual checks, testing, and timely replacements contribute to the longevity and reliability of the circuit breakers.
Conclusion:
Molded Case Circuit Breakers, with their robust construction, versatile functionality, and broad applications, stand as silent sentinels in the realm of electrical protection. As we navigate the complexities of modern electrical systems, understanding the inner workings and applications of MCCBs becomes key to ensuring not just power distribution but also the longevity and safety of our interconnected world.